Issue
- You do not have an appropriate database for your ESET PROTECT Server installation
- You want to set up a dedicated database user for MS SQL or MySQL
Details
Click to expand
You must create an administrator or root account in an MS SQL or MySQL installation. It is not recommended to use the sa / root (database administrator) account for the ESET PROTECT Server to connect to the database. You should create a dedicated database user and a dedicated database.
Solution
- MS SQL—Create a database and user for ESET PROTECT On-Prem
- MySQL—Create a database and user for ESET PROTECT On-Prem
Create a database and user for ESET PROTECT On-Prem in MS SQL
Prerequisites
- You must have administrative access to the operating system
- A supported MS SQL Server must be installed and properly configured on Windows (in this example, SQL Server 2019)
- Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio must be installed
- You must have an administrative account in MS SQL and Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio
Create a database
Open the MS SQL Server Management Studio and log in with your administrator account.
In Object Explorer, right-click Databases and select New Database... from the context menu.
Type the database name in the Database name text box. You will need this name during the ESET PROTECT On-Prem installation. For example, you can use the default ESET PROTECT On-Prem database name
era_db.Click OK and continue to the next section to assign a new user to your database.
Create and assign a new user
Open MS SQL Server Management Studio and log in with your administrator account.
In Object Explorer, right-click Security → New → Login.
Type your new user's username in the Login name field. For example, you can use the default ESET PROTECT On-Prem database username
era_user.Select SQL Server authentication.
Set your new password and type it in the Password and Confirm password fields. You can also set other properties here, if needed.
Select User Mapping and select the check box next to the database you created. Your username should appear in the column User next to your selected database. Select the check box next to db_owner in the Database role membership section. Click OK to save your changes.
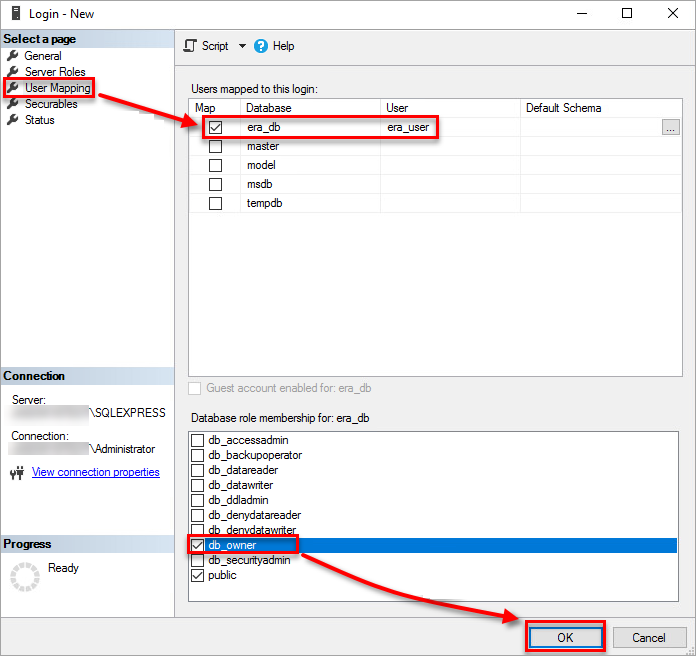
Figure 1-1
Create a database and user for ESET PROTECT On-Prem in MySQL
Prerequisites
- You must have administrative access to the operating system
- A supported MySQL Server must be installed and properly configured on Windows
- You must have an administrator account in MySQL
- In this article, we use HeidiSQL as the administration tool; however, you can use a different tool or the command line, but some steps may differ
Create a database
Open your MySQL administration tool and log in to the local database using the root account and password. Set the Hostname as 127.0.0.1.
Click Open to open your session. Right-click the database root and select Create new → Database from the context menu.
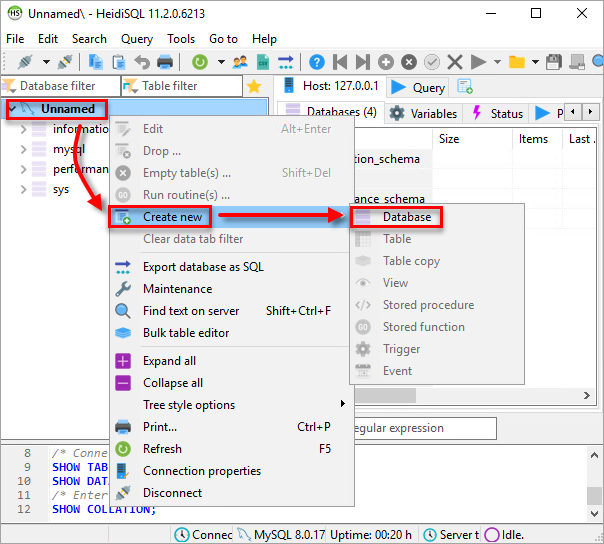
Figure 2-1 - Type a name for your database. For example, you can use the default ESET PROTECT On-Prem database name
era_db. Click OK.
Create and assign a new user
Open your MySQL administration tool and log in to the local database using a root account.
Set the Hostname to 127.0.0.1.
Click Tools → User manager.
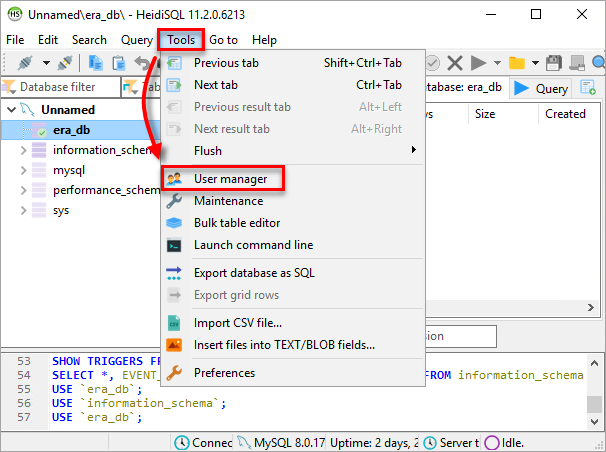
Figure 2-2 Click Add and provide details for the new database user:
- Type the new user's name into the Username field—for example, you can use the default ESET PROTECT On-Prem database username
era_user - Set the From host value to Access from everywhere (%)
- Set a secure password in the Password and Repeat password text boxes
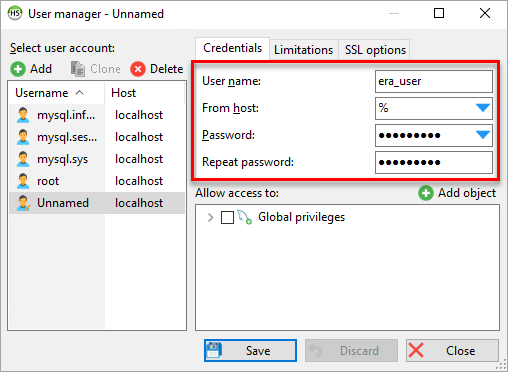
Figure 2-3
- Type the new user's name into the Username field—for example, you can use the default ESET PROTECT On-Prem database username
Click Add object, select the database you created earlier and click OK.
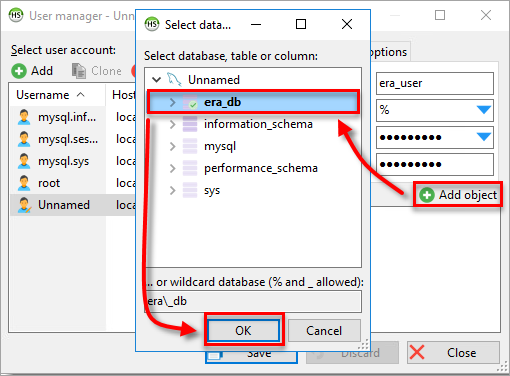
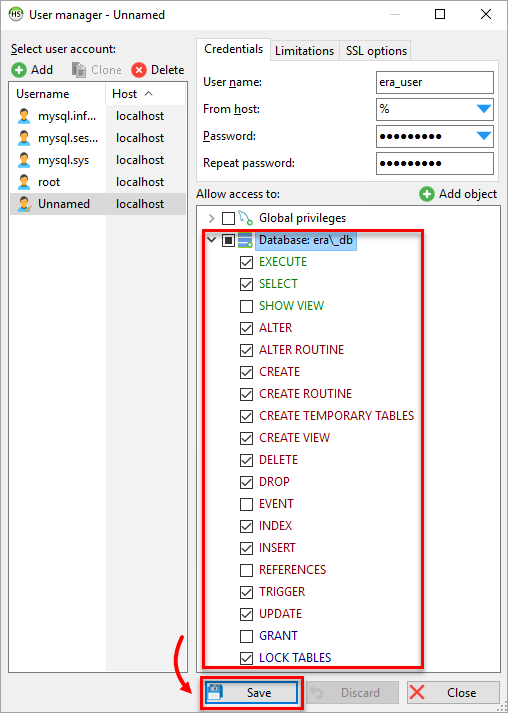
Figure 2-4 Under Allow access to, select the new database and mark the following properties:
- EXECUTE
- SELECT
- ALTER
- ALTER ROUTINE
- CREATE
- CREATE ROUTINE
- CREATE TEMPORARY TABLES
- CREATE VIEW
- DELETE
- DROP
- INDEX
- INSERT
- TRIGGER
- UPDATE
- LOCK TABLES
Click Save to confirm the user settings.
Click Clone. For the newly copied user, change the value of From host to Access from server location only (localhost) and click Save.
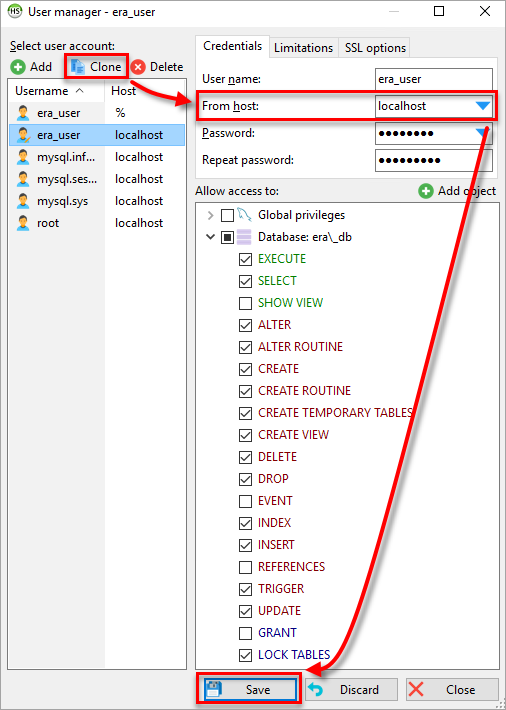
Figure 2-6
In the end, you have two users with the same name—one with access from anywhere and one with localhost access only.