Issue
Details
Click to expand
The ESET firewall monitors and controls communication within the local network or the internet. Using predefined rules, the firewall analyzes communication activities and decides which traffic to allow or block. There are five firewall modes to choose from, each designed for a specific type of application or level of security. To change the behavior of your firewall, choose the filtering mode that best matches your needs.
Solution
Change the firewall filtering mode on individual client workstations
![]() ESET PROTECT On-Prem users: Perform these steps in ESET PROTECT On-Prem
ESET PROTECT On-Prem users: Perform these steps in ESET PROTECT On-Prem
-
Click Setup → Network.
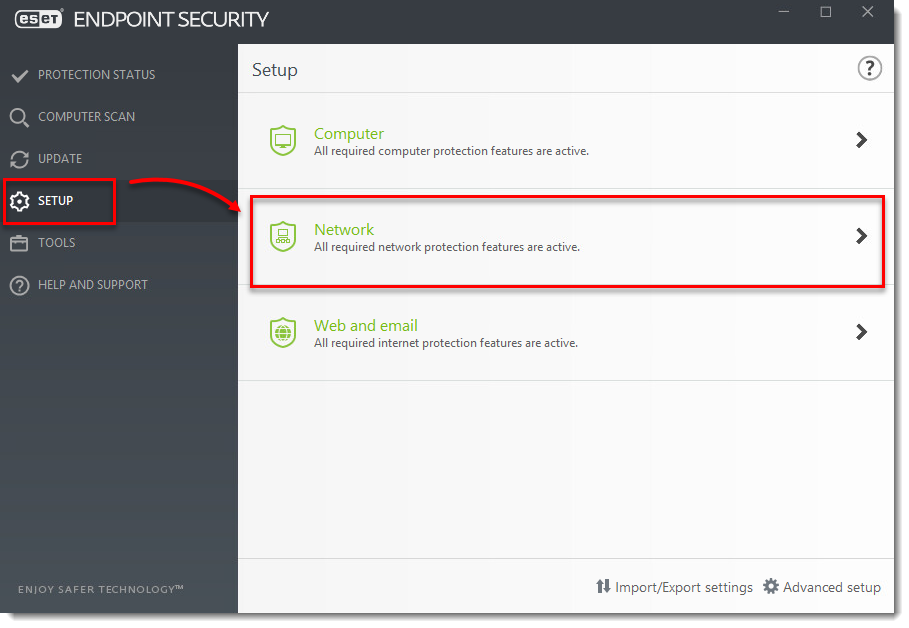
- Click the gear icon next to Firewall and select Configure from the drop-down menu.
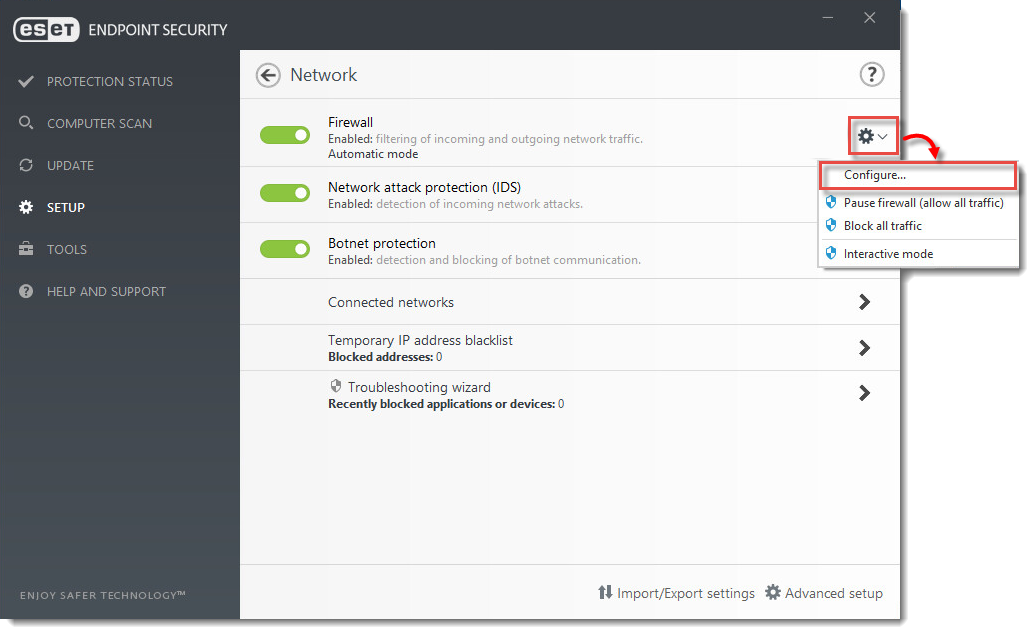
- Click Firewall, select your desired filtering mode from the Filtering mode drop-down menu and click OK.
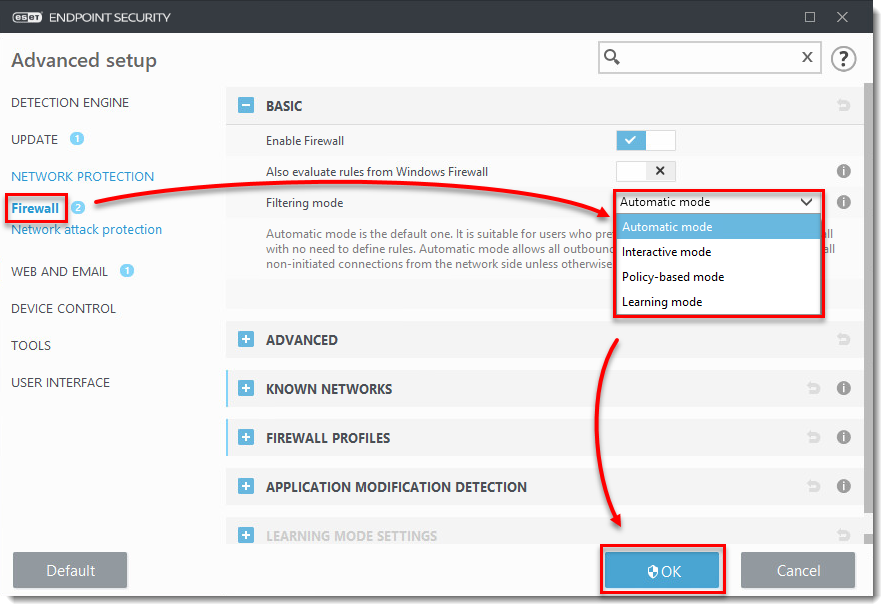
Explanation of filtering modes
Automatic mode — In Automatic mode, network communication is automatically controlled by settings defined by the user. In some earlier versions, it was possible to select Automatic mode with exceptions. Later versions of ESET Endpoint Security always incorporate any user-defined exceptions that have been created automatically when operating in Automatic mode.
After connecting to a network, ESET Endpoint Security will prompt you to define whether that network is included in a trusted zone. Communication in a trusted zone is allowed in both directions. Communication in a restricted zone is allowed only for applications that establish outgoing connections. Once an application initiates an outgoing connection, it is allowed to create an incoming connection in Automatic mode. Automatic mode requires no user interaction (except when connecting to a new network) and does not use any predefined rules out-of-the-box.
Automatic mode with exceptions (user-defined rules)—The same behavior as Automatic mode, but the administrator or user can create custom rules.
Interactive mode—In Interactive mode, network communication is handled according to pre-defined rules. If there is no rule available for a connection, the user is prompted to allow or deny the connection. After some time, the user will have created a group of rules fitting his or her needs. Use caution when choosing this mode in a corporate environment because users who do not pay attention to each prompt can accidentally create a rule that might expose them to risk or hinder their ability to communicate over the network.
Policy-based mode—In Policy-based mode, network communication is handled according to rules defined by the administrator. If there is no rule available, the connection is automatically blocked and the user sees no warning message. We recommend that you only select Policy-based mode if you are an administrator who intends to control network communication and you are sure you know which applications should be allowed or denied.
Learning mode—Learning mode should only be used if you are an experienced user in a controlled environment because it does not require user approval to create permanent rules and can expose your computer to increased risk.
Learning mode allows all activity and automatically creates and saves rules based on user behavior; it offers a less user-intensive initial configuration of the Firewall. No user interaction is required. Learning mode is not secure, and should only be used until all rules for required communications have been created. The Firewall should then be set to Automatic mode with exceptions or Policy-based mode.